-
增材制造技术在载人航天工程中的应用与展望
刘洋,周建平,张晓天
2023,49(1):83-91
doi:10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0455
 摘要
摘要近年来,增材制造技术在载人航天工程中的应用迅速发展。对熔融沉积成型技术、激光选区熔化技术、线材电弧增材制造技术、热喷涂增材技术、月壤增材制造技术等用于载人航天工程的增材制造技术及这些技术的应用领域进行了总结。对增材制造技术在在轨制造飞行器替换件、制造大型桁架等难以在地面制造或发射的部件、制造飞行器复杂部件等应用领域进行了总结。提出未来载人航天工程技术的增材制造中应发展适合载人航天工程的材料体系,应研究微重力环境下的增材制造技术,同时未来还应发展相关工艺。
-
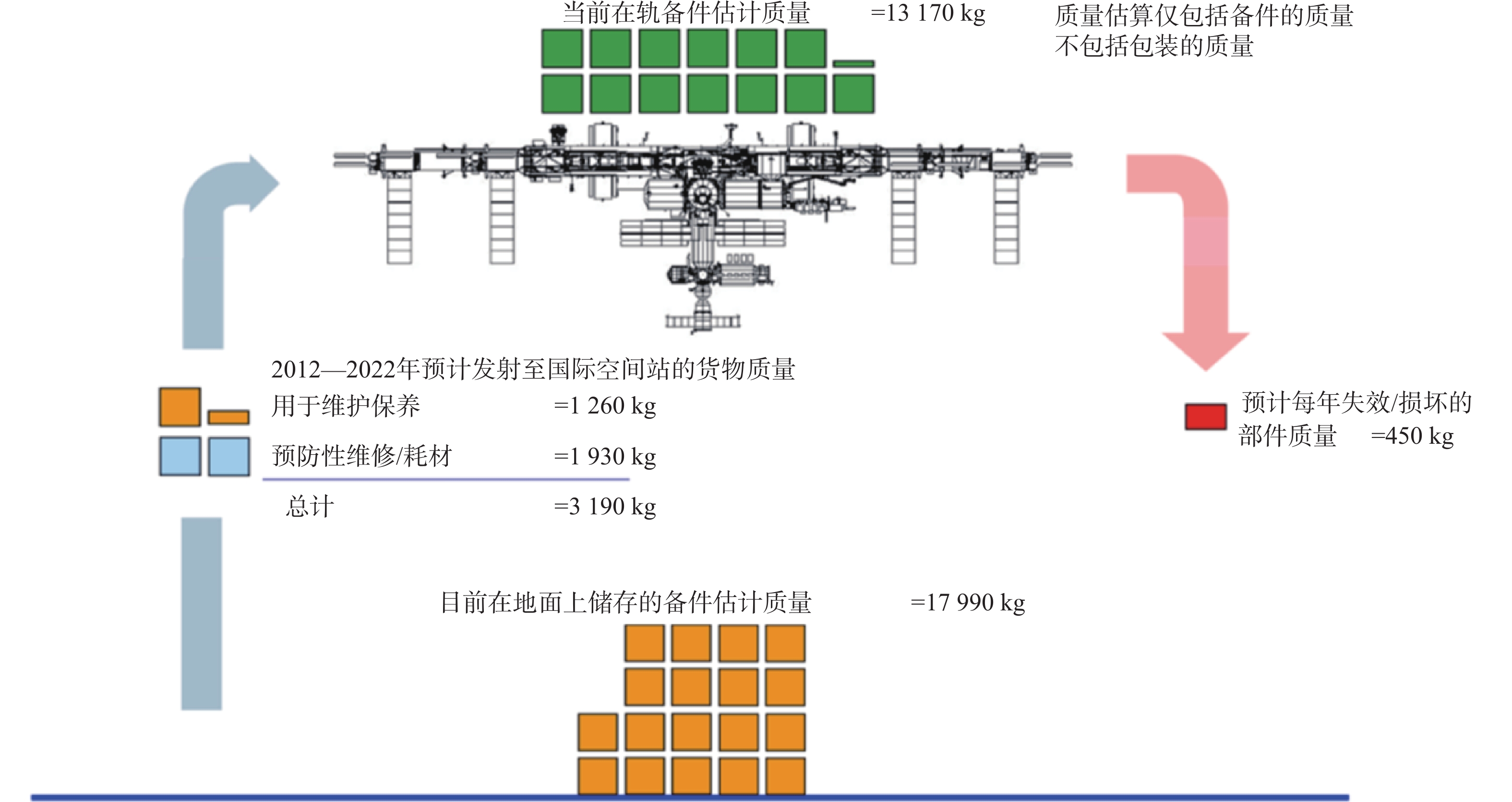
基于Transformer模型的滚动轴承剩余使用寿命预测方法
周哲韬,刘路,宋晓,陈凯
2023,49(2):430-443
doi:10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0247
 摘要
摘要准确的滚动轴承剩余使用寿命(RUL)预测对保证机械安全运行和减小维修损失起着至关重要的作用。为提高滚动轴承RUL预测准确率,提出一种基于Transformer模型的轴承RUL预测方法,充分利用其自注意力机制与编码器-解码器结构的优势,解决轴承RUL预测中序列过长而导致的记忆力退化问题,挖掘出输入特征与轴承RUL之间复杂映射关系。同时,采用三角函数变换与累积变换来修正输入特征的单调性与趋势性,使其能更好地表征滚动轴承的退化过程。在PHM2012数据集上的实验结果表明:所提方法相比于对比方法平均绝对误差分别降低了9.25%、28.63%、34.14%,平均得分分别提高了2.78%、19.79%、29.38%;在XJTU-SY数据集上的实验结果表明,所提方法相比于对比方法均方根误差降低了17.4%,平均得分提高了18.6%,进一步证明了其可行性与优越性
-
-
热障涂层隔热机理分析及有效性判据
刘洋, 杜泽群, 李海旺,由儒全
2022,37(11):2430-2439
doi:10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20220309
 摘要
摘要建立了一维对流-导热模型,经理论推导、分析验证得到了热障涂层隔热有效性判据:当涂层热阻大于无涂层时高温燃气侧换热热阻时,涂层总能使叶片金属基体外表面温度降低,起到隔热效果;反之,则喷涂热障涂层(TBC)后外部燃气侧表面传热系数存在临界值,只有该表面传热系数小于临界值,热障涂层才能起到隔热效果,否则涂层起不到隔热效果,甚至会恶化叶片换热。热障涂层自身温降与有无涂层前后叶片金属基体外表面温降成比例关系,建立了以叶片金属基体外表面温度为基础的新的涂层隔热效果评价机制。
-
In vitro fluidic systems: Applying shear stress on endothelial cells
Fanzhe Meng, Hong Cheng, Jiayi Qian, Xinyuan Dai, Yan Huang, Yubo Fan
2022,100143
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100143
 摘要
摘要Endothelial cells (ECs) that reside on the surface of blood vessels are constantly exposed to mechanical stimulation, including shear stress. Fluid shear stress (FSS) controls multiple physiological processes in ECs, regulating various pathways that maintain vascular tone and homeostasis function. The complexity of in vivo biological systems raises a demand for better in vitro techniques, which can generate FSS to closely mimic the cellular microenvironment. Through the rational design and use of flow chamber devices, in vitro fluidic systems are critical for a deeper understanding of endothelial responses to various shear conditions. The paper describes principal types of FSS systems, including functional attributes, development process and recent experiments on ECs. Finally, we prospect their possible contribution in the field of endothelial diseases.
-
机场跑道水泥混凝土道面板尺寸分析
张献民, 李梦晓, 陈宇, 李长辉, 徐博庆
doi:doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0646
 摘要
摘要中国机场通常采用板宽不超过5 m的水泥混凝土道面板,国际上已有机场采用板宽6 m以上的水泥混凝土道面板。相比大尺寸水泥混凝土道面板,小尺寸道面板容易产生病害。为了研究道面板尺寸对道面性能的影响,基于弹性层状理论体系建立道面结构有限元模型,通过改变水泥混凝土道面板平面尺寸,研究了考虑温度梯度时飞机荷载作用下道面板内的应力变化。通过某机场实例分析了温度梯度和飞机荷载共同作用下道面板平面尺寸对道面使用寿命的影响,结果表明:道面板内应力受温度梯度影响较大,常见机型荷载作用下,夏季道面板内拉应力25%以上是由温度梯度荷载造成;不同尺寸道面板在相同荷载作用下,道面产生的损伤量不同,设计过程中加入道面板温度应力计算,选择合适的道面板尺寸,可以显著提高水泥混凝土道面的预期使用寿命。
-
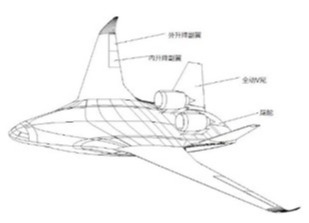
Stability characteristics and arworthiness requirements of blended wing body aircraft with podded engines
Lixin WANG,Ning ZHANG,Hailiang LIU,Ting YUE.
doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2021.09.002
 摘要
摘要Blended-Wing-Body (BWB) aircraft have a relatively short fuselage and no horizontal tail, and they usually adopt podded engines and a V tail instead of a vertical tail. Generally, BWB aircraft have decreased longitudinal and directional static stability and damping. In this paper, the three-axis static and dynamic stability characteristics of an example BWB aircraft with podded engines are studied. According to the differences in flight characteristics of BWB aircraft and conventional aircraft, the different airworthiness requirements for BWB aircraft are analyzed: first, based on current airworthiness regulations and transport aircraft flying quality specification, the relaxation requirement of longitudinal static stability for BWB aircraft is studied; second, the influences of podded engines on longitudinal trim, attitude and trajectory responses and maximum directional control power requirement of BWB aircraft are analyzed; third, the changes in the proportional relationships...
-
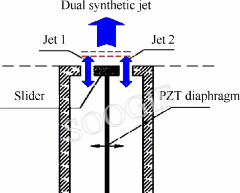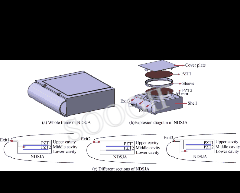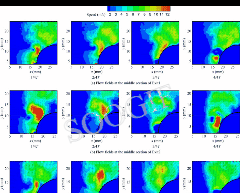
Novel roll effector based on zero-mass-flux dual synthetic jets and its flight test
Zhenbing LUO, Zhijie ZHAO, Jiefu LIU, et al.
doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2021.08.015
 摘要
摘要The autonomous and controllable Dual Synthetic Jet Actuator (DSJA) is firstly integrated into the Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), and flight tests without the deflection of rudders are carried out to verify the viability of DSJA to control the attitudes of UAV during cruising. DSJA is improved into an actuator with two diaphragms and three cavities, which has higher energy levels. Actuators, differentially distributed on both sides of the wings, are installed on the trailing edge close to the wing tips. Flight tests, containing Differential Circulation Control (DCC) using double-side actuators, Positive Circulation Control (PCC) using left-side actuators and Negative Circulation Control (NCC) using right-side actuators, are implemented at cruising speed of 25 m/s. Results show that roll attitude control without rudders could be realized by DSJAs. DCC and NCC can generate the rightward roll and yaw angular velocity...
-
1
The role of mechanoreceptors in acupuncture
Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices2023,21(3)
-
2
MV-mediated biomineralization mechanisms and treatments of biomineralized dis...
Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices2023,21(3)
-
3
SR-AFU: super-resolution network using adaptive frequency component upsamplin...
Frontiers of Computer Science2023,21(3)
-
4
Unsupervised statistical text simplification using pre-trained language model...
Frontiers of Computer Science2023,21(3)
-
5
推力矢量型V/STOL飞行器动态过渡过程的操纵策略优化
航空动力学报2023,21(3)
-
6
耦合传热下激波对超声速气膜冷却影响
航空动力学报2023,21(3)
-
北京航空航天大学学报
-
北京航空航天大学学报(社会科学版)
-
复合材料学报
-
集成电路与嵌入式系统
-
航空学报
-
Chinese Journal of Aeronautics
-
航空动力学报
-
Frontiers of Computer Science
-
Propulsion and Power Research
-
Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices
-
Digital Twin
-
Electromagnetics Science and Technology
-
Congnitive Semantics
-
The Journal of the Air Transport Research Society
-
航空知识
-
问天少年
-
Chain
-
Virtual Reality & Intelligent Hardware
-
International Journal of Modeling Simulation and Scientific Computing
-
International Journal of Service and Computing Oriented Manufacturing
-
Mathematics in computer science
-
Atlantis Highlights in Engineering
-
Mathematical Blosciences and Engineering
-
Materials LAB
-
Journal of Economy and Technology
-
Digital Engineering
-
Guidance Navication and Control
-
Visual Computing for Industry Biomedicine and Art
-
图学学报