-
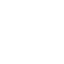
The role of mechanoreceptors in acupuncture
Shu Han
Volume 17, March 2023, 100207
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2023.100207
 摘要
摘要Acupuncture has been used for centuries to heal the body; it is essential to comprehend the mechanism of acupuncture within the modern medical framework. By far much research provided a modern scientific understanding of how acupuncture works, most of them indicated that nervous system is involved. However, few studies have been conducted on how acupuncture trigger the nervous system. When the thin needle inserts the acupoint, the mechanical stress generated by acupuncture is the key factor of acupuncture effect. The first peripheral receptors activated in this process are mechanoreceptors, which are sensitive to mechanical forces. The purpose of this review is to explore the connection between the mechanoreceptors located in the skin and subcutaneous tissues and the acupuncture therapy. It also attempts to clue the possible roles of mechanoreceptors in the skin surface and subcutaneous tissue during the acupuncture manipulation and electroacupuncture.
-
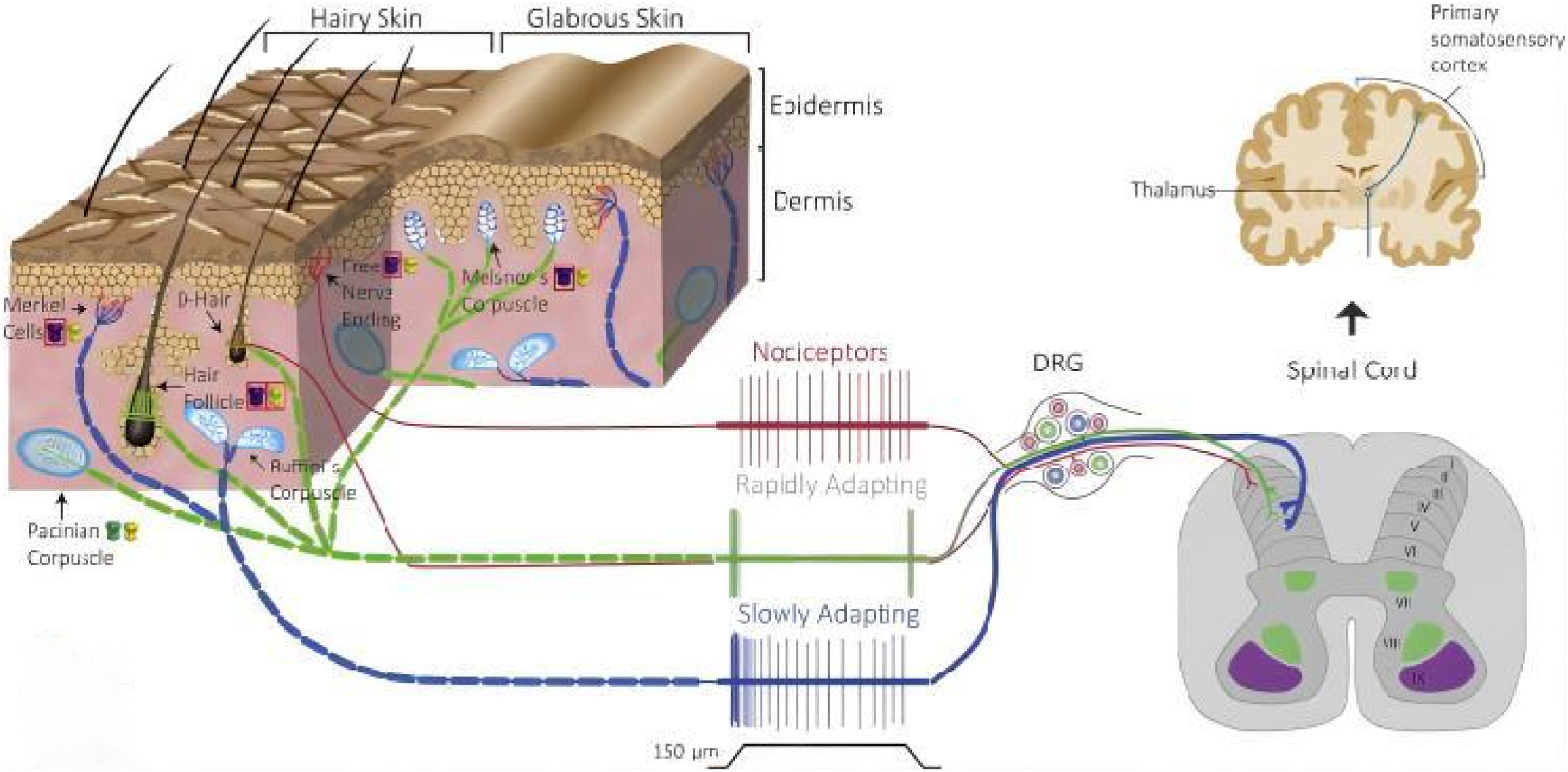
MV-mediated biomineralization mechanisms and treatments of biomineralized diseases
Xuan Li, Wei Zhang, Yubo Fan, Xufeng Niu
Volume 17, March 2023, 100198
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100198
 摘要
摘要As the quality of life improves, people pay more and more attention to health. They are concerned about the causes of diseases, and seek better treatments. The most common diseases are biomineralized diseases, four different kinds of typical examples among which are selected to elaborate their mechanisms and existing treatments. Whether it is tooth and bone in physiological mineralization or cartilage and blood vessel in pathological mineralization, they are all related to matrix vesicle (MV)-mediated biomineralization. MV-mediated biomineralization is the initial stage of biomineralization and the nucleation site mediating collagen mineralization. Definition, composition, biogenesis, and action mechanism of MVs are refined and expounded, especially a novel biomineralization pathway similar to exosome (EX) origin. Four differences are summarized to distinguish MVs and EXs.
-

SR-AFU: super-resolution network using adaptive frequency component upsampling and multi-resolution features
Ke-Jia CHEN, Mingyu WU, Yibo ZHANG, Zhiwei CHEN
2023, 17(1): 171307
doi:10.1007/s11704-021-0562-y
 摘要
摘要Image super-resolution (SR) is one of the classic computer vision tasks. This paper proposes a super-resolution network based on adaptive frequency component upsampling, named SR-AFU. The network is composed of multiple cascaded dilated convolution residual blocks (CDCRB) to extract multi-resolution features representing image semantics, and multiple multi-size convolutional upsampling blocks (MCUB) to adaptively upsample different frequency components using CDCRB features. The paper also defines a new loss function based on the discrete wavelet transform, making the reconstructed SR images closer to human perception. Experiments on the benchmark datasets show that SR-AFU has higher peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), significantly faster training speed and more realistic visual effects compared with the existing methods.
-

Unsupervised statistical text simplification using pre-trained language modeling for initialization
Jipeng QIANG, Feng ZHANG, Yun LI, Yunhao YUAN, Yi ZHU, Xindong WU
2023, 17(1): 171303
doi:10.1007/s11704-022-1244-0
 摘要
摘要Unsupervised text simplification has attracted much attention due to the scarcity of high-quality parallel text simplification corpora. Recent an unsupervised statistical text simplification based on phrase-based machine translation system (UnsupPBMT) achieved good performance, which initializes the phrase tables using the similar words obtained by word embedding modeling. Since word embedding modeling only considers the relevance between words, the phrase table in UnsupPBMT contains a lot of dissimilar words. In this paper, we propose an unsupervised statistical text simplification using pre-trained language modeling BERT for initialization. Specifically, we use BERT as a general linguistic knowledge base for predicting similar words. Experimental results show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art unsupervised text simplification methods on three benchmarks, even outperforms some supervised baselines.
-

推力矢量型V/STOL飞行器动态过渡过程的操纵策略优化
周涛, 王子安, 龚正, 佘崇民, 赵彤, 张同任
2023, 38(2):408-419
doi:10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20210412
 摘要
摘要针对推力矢量型垂直/短距起降(vertical/short takeoff and landing, V/STOL)飞行器的动态过渡过程模型,综合考虑过渡走廊限制、操纵冗余及不同起降任务需求指标,研究最优过渡操纵策略。考虑V/STOL 飞行器的喷射气流效应,对飞行器进行全量动力学建模。利用可达平衡集方法,建立通用过渡走廊计算框架。设计了能够在V/STOL过渡段和高速飞行间平稳过渡的操纵方式。将推力矢量飞行器的动态倾转过渡过程转化为非线性动态最优控制问题,根据不同起降任务特点建立合理的指标和约束,采用直接转换法和序列二次规划算法进行求解,得出不同任务特点下的最优操纵策略与过渡过程。采用可达平衡集计算过渡走廊的方法,不仅不受飞行器类型的限制,更简化了构造过程,具有良好的通用性与鲁棒性。以光滑过渡为目标的优化结果使得飞行员在飞行器过渡过程中的操纵量变化大幅减小,从而使得飞行员能更加专注于对飞行器运动的操纵;以距离更短为目标的优化结果则使得降落过程的飞行距离缩短了30%左右。从操纵策略出发的优化结果使得驾驶员能够更好掌握操纵关注点及边界,增加了整个动态过渡过程的安全性。
-

耦合传热下激波对超声速气膜冷却影响
向纪鑫, 李志强, 刘鹏, 王菡
2023, 38(2):344-353
doi:10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20210413
 摘要
摘要针对离散孔式超声速平板气膜冷却,在主流区引入楔角形成激波环境,以研究激波与超声速气膜之间的相互作用。通过计算楔角在0°、15°、20°和25°产生的四种激波强度下,超声速气膜与高温壁面的耦合传热。所得结果表明:适当强度的激波能够抑制气膜入射后产生的反向涡旋对,降低主流对气膜的卷吸,增大壁面平均H2摩尔分数并降低壁面温度。对金属层温度场的分析表明,壁面冷却效果随着激波角的增加而先增加后降低,其中楔角为20°时的流场结构最有利于壁面温度保护。小楔角生成的激波在低冷流马赫数下对冷却效果的改善更明显,大楔角则在高冷流马赫数下更明显,热障涂层(TBC)不影响这种变化趋势;激波的存在削弱了TBC的影响范围。可以揭示超声速气膜在耦合传热条件下的传热机理,为超声速气膜冷却的设计提供参考,或为现有超声速气膜冷却结构的优化提供依据。
-
适用于复杂流动的热气动弹性降阶建模方法
王梓伊, 张伟伟, 刘磊, 杨肖峰
2023, 44(4): 126807-126807
doi:10.7527/S1000-6893.2022.26807
 摘要
摘要针对高超声速巡航类飞行器面临的复杂流动下的热气动弹性问题,发展了一种时变热模态适用的非定常气动力降阶模型,建立了基于流-热-固时空耦合分析策略的热气动弹性分析方法,对高超声速飞行器前体进气压缩面进行了实际飞行加热过程的时变颤振分析。结果表明,在局部高热流载荷下,压缩面固有模态频率和振型随时间发生了大幅度变化,而所建方法能够适应上述变化,在获得高置信度非定常广义气动力的同时,避免了重复性的非定常气动力数值计算,可将热颤振分析中的气动力计算效率提升若干量级;此外,在达到热平衡后,进气压缩面的颤振动压降为初始时刻的0.64%,使得飞行包线大幅收窄。相关方法有效缓和了热气动弹性分析效率与精度的矛盾,提升了热气动弹性问题的工程分析能力。
-
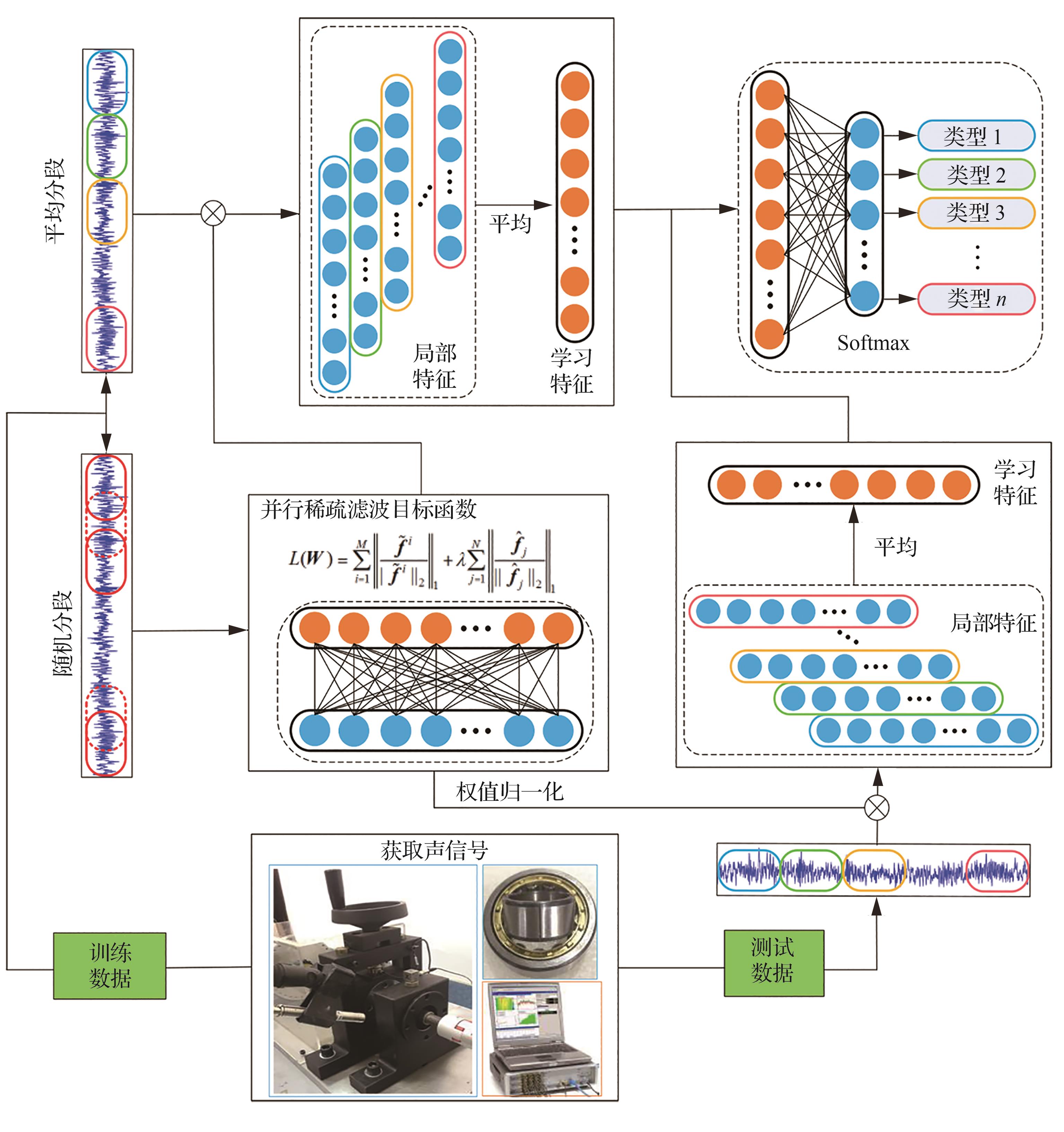
并行稀疏滤波在轴承声信号下的故障诊断
王金瑞, 季珊珊, 张宗振, 初振云, 韩宝坤, 鲍怀谦
2023, 44(4): 426887-426887
doi:10.7527/S1000-6893.2022.26887
 摘要
摘要振动信号是航空发动机故障监测的常用信号。由于航空发动机结构复杂,对振动传感器的布置要求日益严格。声学信号以其非接触式、易布置、低成本的优点,在轴承智能故障诊断中引起了广泛的关注。然而,由于航空发动机内声信号所处的环境噪声较强,传统的轴承故障诊断方法无法实现精确的特征提取。为此,研究有效的特征提取方法实现轴承声信号下的智能故障诊断显得尤为重要。稀疏表示是智能故障诊断中的一个研究热点,在稀疏特征提取方面显示出强大的力量。对强噪声下的声信号进行有效的稀疏特征提取,可为轴承的非接触式故障诊断提供解决路径。提出一种基于并行稀疏滤波的轴承故障诊断方法,能够实现对轴承声信号的稀疏特征提取。并行稀疏滤波通过在传统稀疏滤波的基础上增加另一个归一化方向来实现进一步的稀疏特征提取,然后采用权值归一化方法约束训练得到的权值矩阵。最后,通过仿真和实验数据验证了所提方法的优越性。结果表明,并行稀疏滤波能够实现轴承声信号的有效稀疏特征提取和精准分类,可用于声学信号下的轴承智能故障诊断。
-
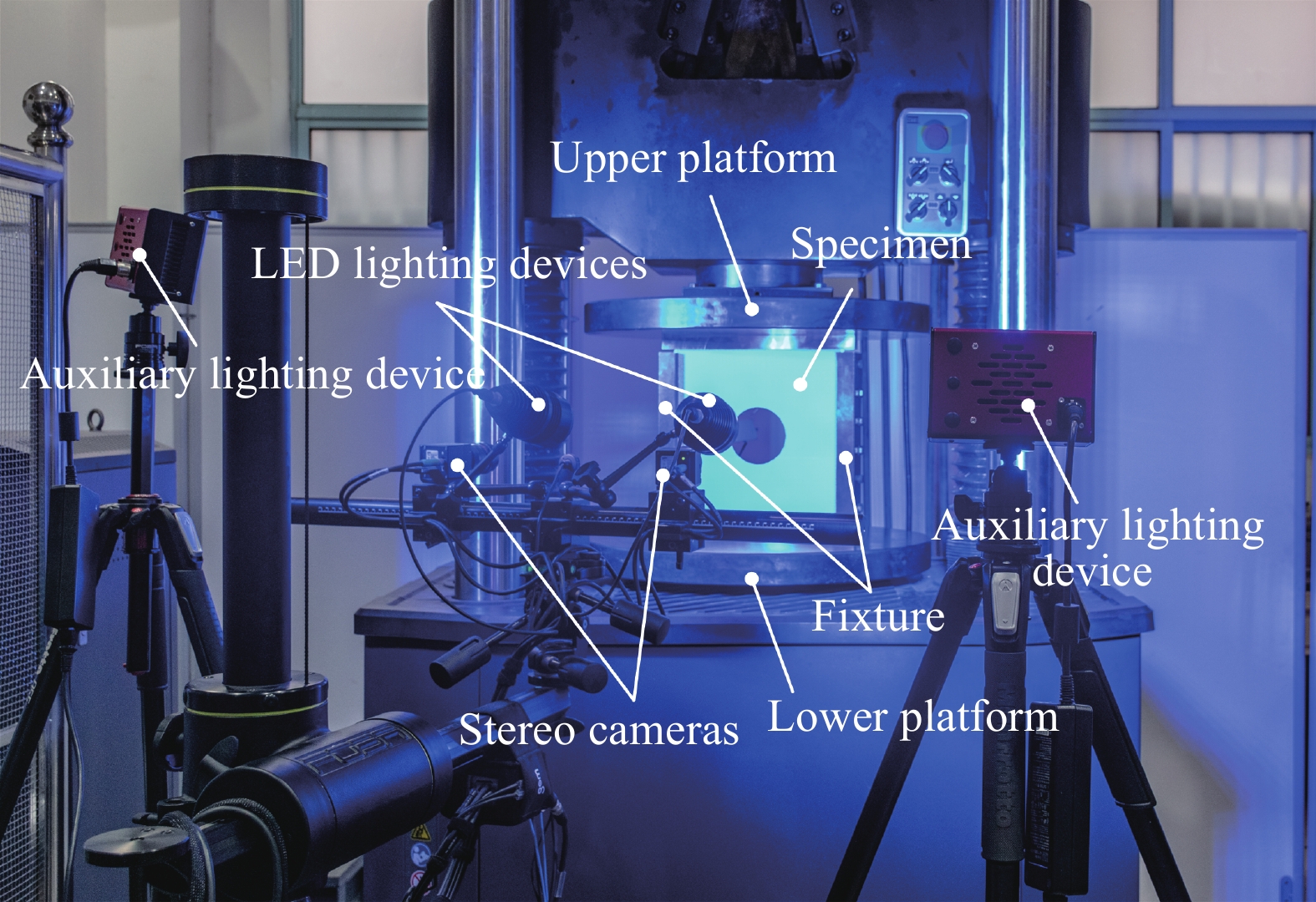
变刚度复合材料平板与开孔板屈曲性能试验验证与数值仿真
张雅会, 陈普会, 孔斌
2023, 40(4): 2450-2462
doi:10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220000.000000
 摘要
摘要为验证基于丝束曲线铺放的变刚度设计在改善典型航空结构屈曲性能中的应用潜力,设计并制造了变刚度复合材料平板和开孔板试件。通过应变片和非接触式三维光学测量系统,全面地测量了试件受单轴压缩载荷过程中的面外位移和载荷方向应变。试验结果表明:变刚度平板和开孔板较同构型直线铺层试件屈曲载荷分别提升53.4%和46.6%;试件力学响应相似,均为线性加载至屈曲载荷后刚度大幅折减,变刚度试件后屈曲阶段呈近似线性,而直线铺层试件则连续变化。根据试验方案细化了数值模型,屈曲载荷、面外位移及应变的计算结果与试验结果基本吻合。在此基础上,提取了数值模型中的刚度分布和加载截面载荷分布,阐明了变刚度设计的抗屈曲机制。对于本文试件,采用变刚度设计还可显著提高破坏载荷,并降低侧边载荷,缓解应力集中。
-

羟基磷灰石包覆羟基锡酸钙复合微纳米阻燃剂的制备及其阻燃性能
王增豪, 马益恒, 娄元猛, 董璐铭, 马海云
2023, 40(5): 2684-2693
doi:10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20201028.001
 摘要
摘要羟基锡酸盐是近些年来人们日益关注的新型阻燃剂。本研究从阻燃设计入手,通过化学共沉淀法合成了亚微米级羟基锡酸钙立方体(CSH),并通过高倍模拟体液法原位快速包覆羟基磷灰石(HA),得到羟基磷灰石/羟基锡酸钙(CSH@HA)复合微纳米阻燃剂,并应用于软质PVC的阻燃研究。研究结果表明CSH@HA对PVC展现出优异的阻燃效果。极少量的CSH@HA即能显著提高PVC的极限氧指数,降低PVC燃烧时的热释放速率、热释放量、烟释放量和CO排放量。CSH@HA在PVC降解过程中通过与HCl反应,保护内层CSH,将PVC转化为更为稳定的炭层结构。低填充量CSH@HA还在保持PVC的力学性能的同时提升材料的韧性。本文得到的羟基磷灰石/羟基锡酸钙复合阻燃剂为高效环保阻燃剂的开发提供了思路。
-
1
The role of mechanoreceptors in acupuncture
Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices2023,21(3)
-
2
MV-mediated biomineralization mechanisms and treatments of biomineralized dis...
Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices2023,21(3)
-
3
SR-AFU: super-resolution network using adaptive frequency component upsamplin...
Frontiers of Computer Science2023,21(3)
-
4
Unsupervised statistical text simplification using pre-trained language model...
Frontiers of Computer Science2023,21(3)
-
5
推力矢量型V/STOL飞行器动态过渡过程的操纵策略优化
航空动力学报2023,21(3)
-
6
耦合传热下激波对超声速气膜冷却影响
航空动力学报2023,21(3)
-
北京航空航天大学学报
-
北京航空航天大学学报(社会科学版)
-
复合材料学报
-
集成电路与嵌入式系统
-
航空学报
-
Chinese Journal of Aeronautics
-
航空动力学报
-
Frontiers of Computer Science
-
Propulsion and Power Research
-
Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices
-
Digital Twin
-
Electromagnetics Science and Technology
-
Congnitive Semantics
-
The Journal of the Air Transport Research Society
-
航空知识
-
问天少年
-
Chain
-
Virtual Reality & Intelligent Hardware
-
International Journal of Modeling Simulation and Scientific Computing
-
International Journal of Service and Computing Oriented Manufacturing
-
Mathematics in computer science
-
Atlantis Highlights in Engineering
-
Mathematical Blosciences and Engineering
-
Materials LAB
-
Journal of Economy and Technology
-
Digital Engineering
-
Guidance Navication and Control
-
Visual Computing for Industry Biomedicine and Art
-
图学学报