Medicine in novel technology and devices 70周年校庆专刊

Medicine in novel technology and devices 70周年校庆专刊
Volume 16 December 2022
Medicine in novel technology and devices 70周年校庆专刊
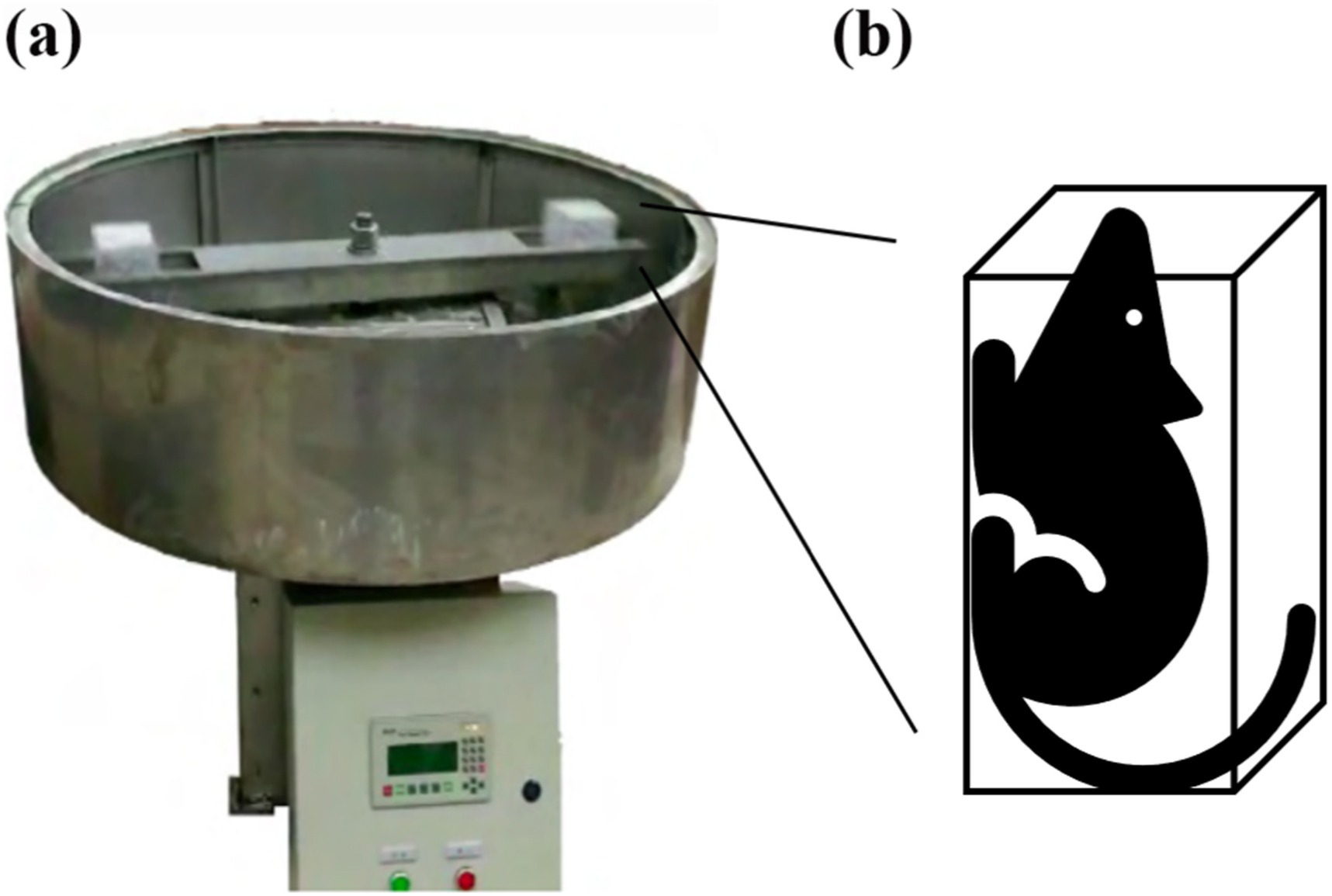
Biomedical response of femurs in male Wistar rat in chronic hypergravity envi...
Lu Yu, Shuping Wei, Biao Han, Lilan Gao, Yang Zhang, Xizheng Zhang,
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100161
2022, 100161
 摘要
摘要
Bone is sensitive to mechanical stimulation and plays a loading-bearing role in the human body. However, regulation of bone biomechanical properties in chronic hypergravity environments is still unclear. In this study, male Wistar rats exposed to chronic hypergravity environments (4×g, 8×g, 10×g, and 20×g) for 4 weeks were set as the hypergravity groups, and rats exposed to the normal gravity as the control group. Morphology parameters and bone remodeling factors were obtained by means of micro-CT, Western blot, and q-PCR. Mechanical properties of femurs were measured utilizing three points bending test and creep test and were fitted into a viscoelastic-viscoplastic constitutive equation. The results indicate osteoporosis occurred in femurs of hypergravity groups.
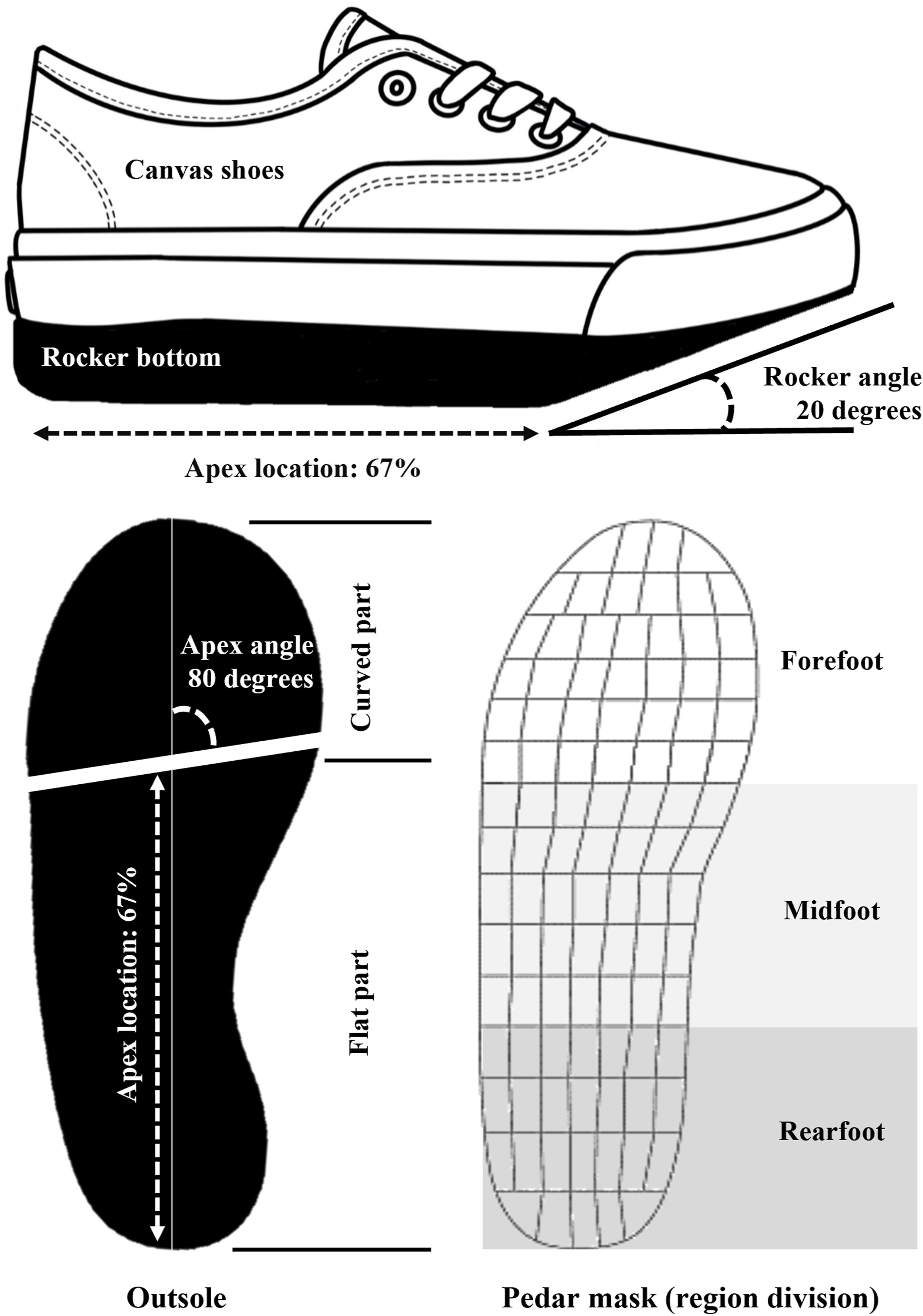
The interaction effects of rocker angle and apex location in rocker shoe desi...
Tony Lin-Wei Chen, Duo Wai-Chi Wong, Yinghu Peng, Yan Wang, Ivy Kwan-Kei Wong, Tsz-Kit Lam, Wing-Kai Lam, Ming Zhang,
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2021.100111
2022, 100111
 摘要
摘要
The influences of rocker shoes on foot biomechanics were controversial because the interaction between two design factors—rocker angle and apex location, was usually omitted. This study investigated the interaction effects of rocker angle and apex location on plantar foot pressure, metatarsophalangeal/ankle angle, and Achilles tendon force during walking. Ten participants performed walking trials under six rocker shoe conditions: 2 rocker angles (mild and severe) × 3 apex locations (distal, standard, and proximal), wherein the plantar foot pressure was measured and the movement data were processed by musculoskeletal modeling to report joint angle and Achilles tendon force. A two-way ANOVA repeated measures was used for statistics. Significant interaction effects were reported in examinations of forefoot pressure, midfoot pressure, and metatarsophalangeal dorsiflexion.
Corneal and scleral biomechanics in ophthalmic diseases: An updated review
Yan Wang, Huazheng Cao
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100140
2022, 100140
 摘要
摘要
Corneal and scleral biomechanical properties have important implications in the maintenance of normal ocular morphology and function. The cornea and sclera compose the outermost layer of the eyeball, forming a sphere with a certain degree of intraocular pressure, and are therefore under dynamic loading conditions. Recently, several major ophthalmic conditions have been shown to be linked to corneal and scleral biomechanical properties, such as ametropia, corneal pathologies, ocular surface disease, and glaucoma. A profound understanding of corneal and scleral biomechanics is essential to clarifying disease pathogenesis, improving diagnostic ability, and developing treatment strategies. This review aims to highlight the role of corneal and scleral biomechanics in ophthalmology and its clinical translation. Specifically, advances and prospects in corneal and scleral biomechanics and possible associated diseases are addressed.
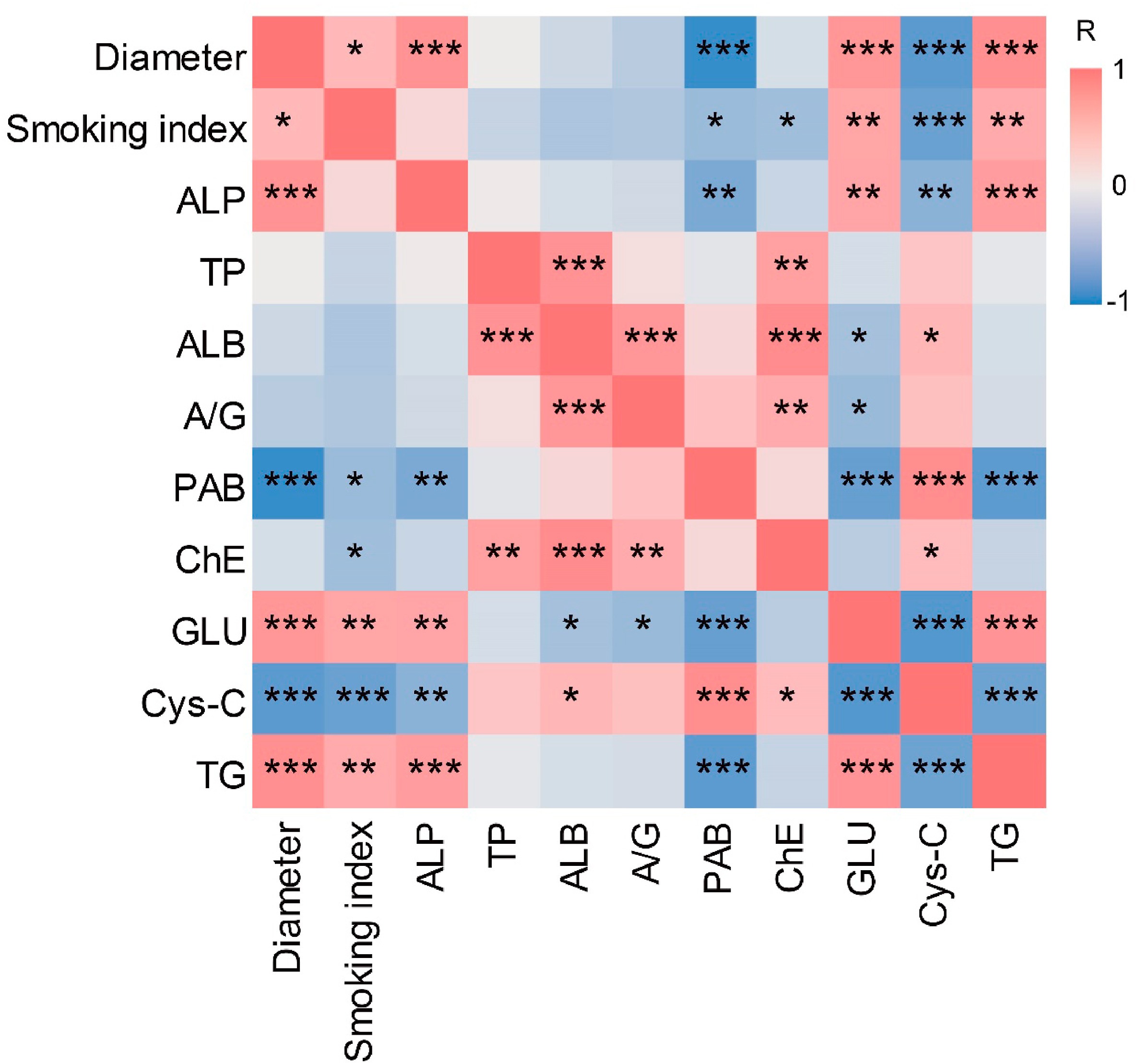
Alterations in gut microbiota and physiological factors associated with abdom...
Kun Zhang, Shiwei Yang, Yingchun Huang, Xian Qin, Kai Qu, Yidan Chen, Lizhao Chen, Juhui Qiu, Yingxue Hao, Guixue Wang
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100122
2022, 100122
 摘要
摘要
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a progressive focal dilatation and weakening of the abdominal aorta, causing 1.3% of all deaths among men aged 65–85 years worldwide. The formation of AAA is a complex process with multiple risk factors. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the relationship of disease severity and physiological factors, and gut microbiota structures in AAA patients. Physiological indicators and fecal 16S rRNA gene sequences from healthy controls and patients with AAA were collected. The correlations between the diameter of the AAA and clinical parameters, and gut microbiota composition were then analyzed separately using multivariable analysis. The diameter of AAA was extremely positively correlated with smoking index, alkaline phosphatase, blood glucose, and blood triglycerides and negatively correlated with prealbumin and Cystatin C.
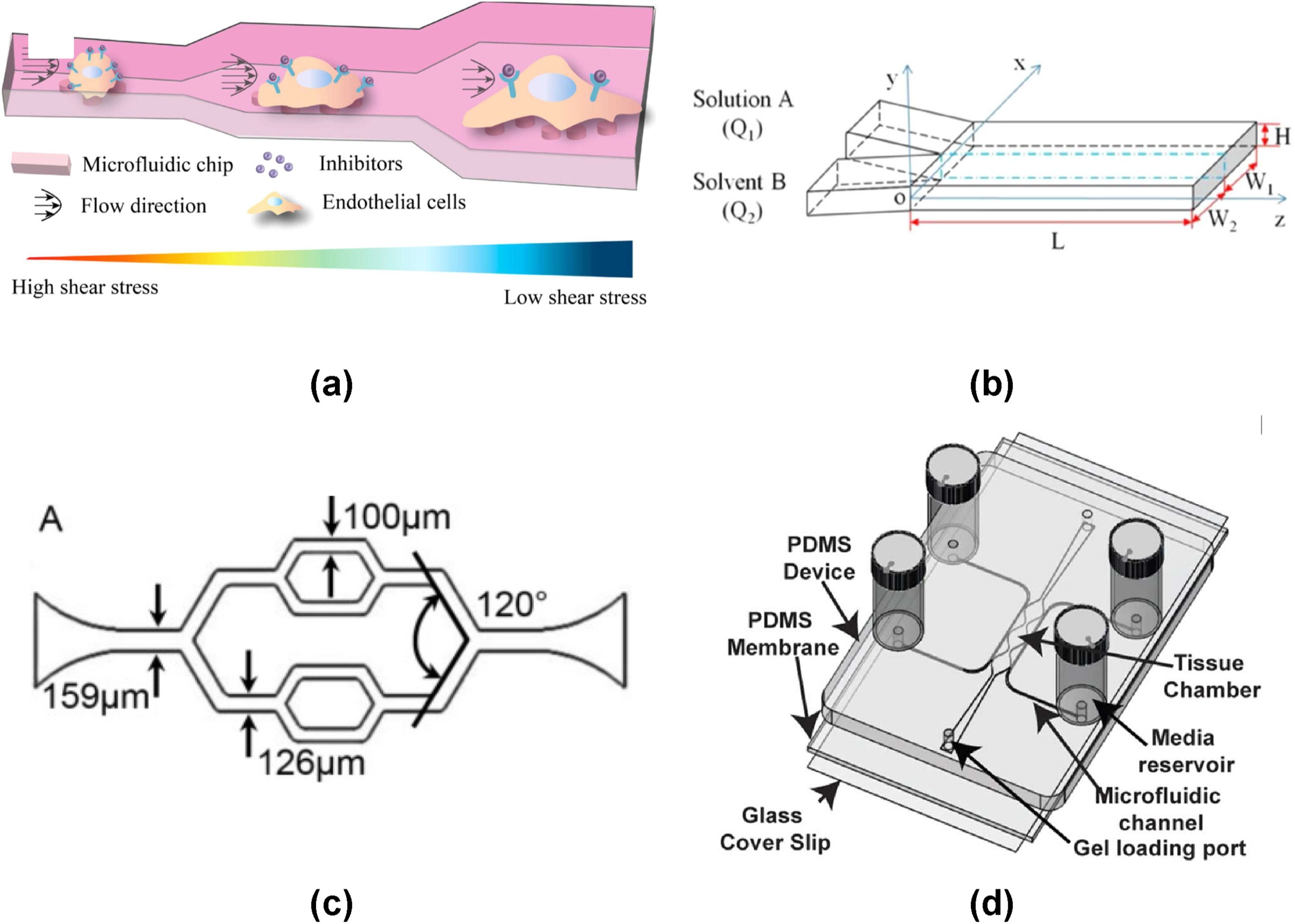
In vitro fluidic systems: Applying shear stress on endothelial cells
Fanzhe Meng, Hong Cheng, Jiayi Qian, Xinyuan Dai, Yan Huang, Yubo Fan
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100143
2022, 100143
 摘要
摘要
Endothelial cells (ECs) that reside on the surface of blood vessels are constantly exposed to mechanical stimulation, including shear stress. Fluid shear stress (FSS) controls multiple physiological processes in ECs, regulating various pathways that maintain vascular tone and homeostasis function. The complexity of in vivo biological systems raises a demand for better in vitro techniques, which can generate FSS to closely mimic the cellular microenvironment. Through the rational design and use of flow chamber devices, in vitro fluidic systems are critical for a deeper understanding of endothelial responses to various shear conditions. The paper describes principal types of FSS systems, including functional attributes, development process and recent experiments on ECs. Finally, we prospect their possible contribution in the field of endothelial diseases.
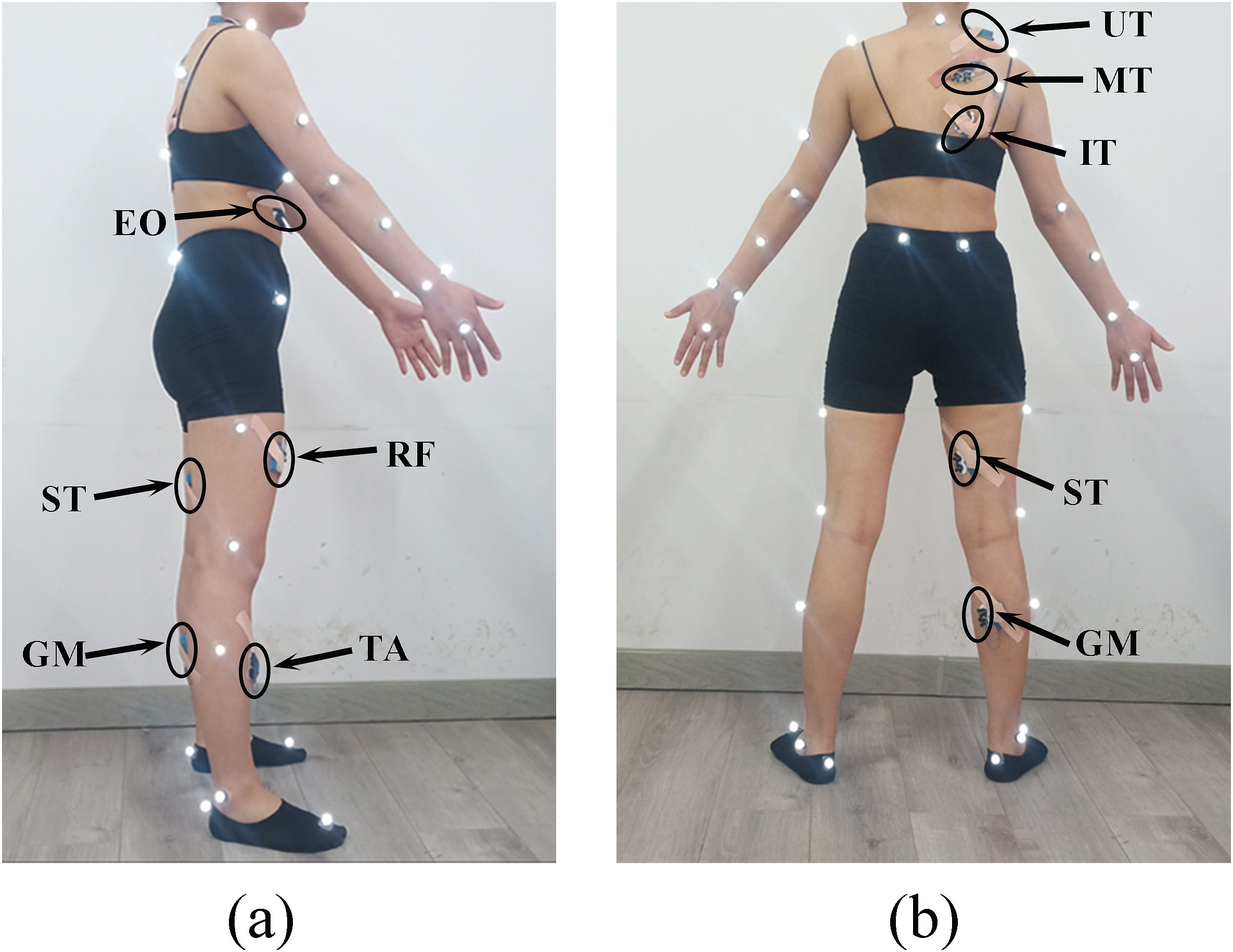
Classification of human movements with and without spinal orthosis based on s...
Chenyan Wang, Xiaona Li, Yuan Guo, Ruixuan Zhang, Weiyi Chen
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100165
2022, 100165
 摘要
摘要
Spinal orthoses were designed to correct poor posture; however, they may restrict trunk movements at all times, making daily activities difficult. Detecting trunk movements can provide instructions for adjusting the stiffness of the spinal orthosis. This study evaluated the feasibility of identifying movements based on surface electromyography (sEMG) signals. Ten participants were tested for different movements with two different modalities: motion without the spinal orthosis (Normal) and with the spinal orthosis (Spinal orthosis). The sEMG signals were collected from eight muscles using surface electrodes during four movements [flexion-extension, lateral bending, axial rotation, and stand to sit to stand]. Four time domain features were extracted, with a total of 32 feature vectors. The principal component analysis (PCA) method was adopted to feature selection, and it was found that eight feature dimensions can make cumulative explained variance exceed 95%.
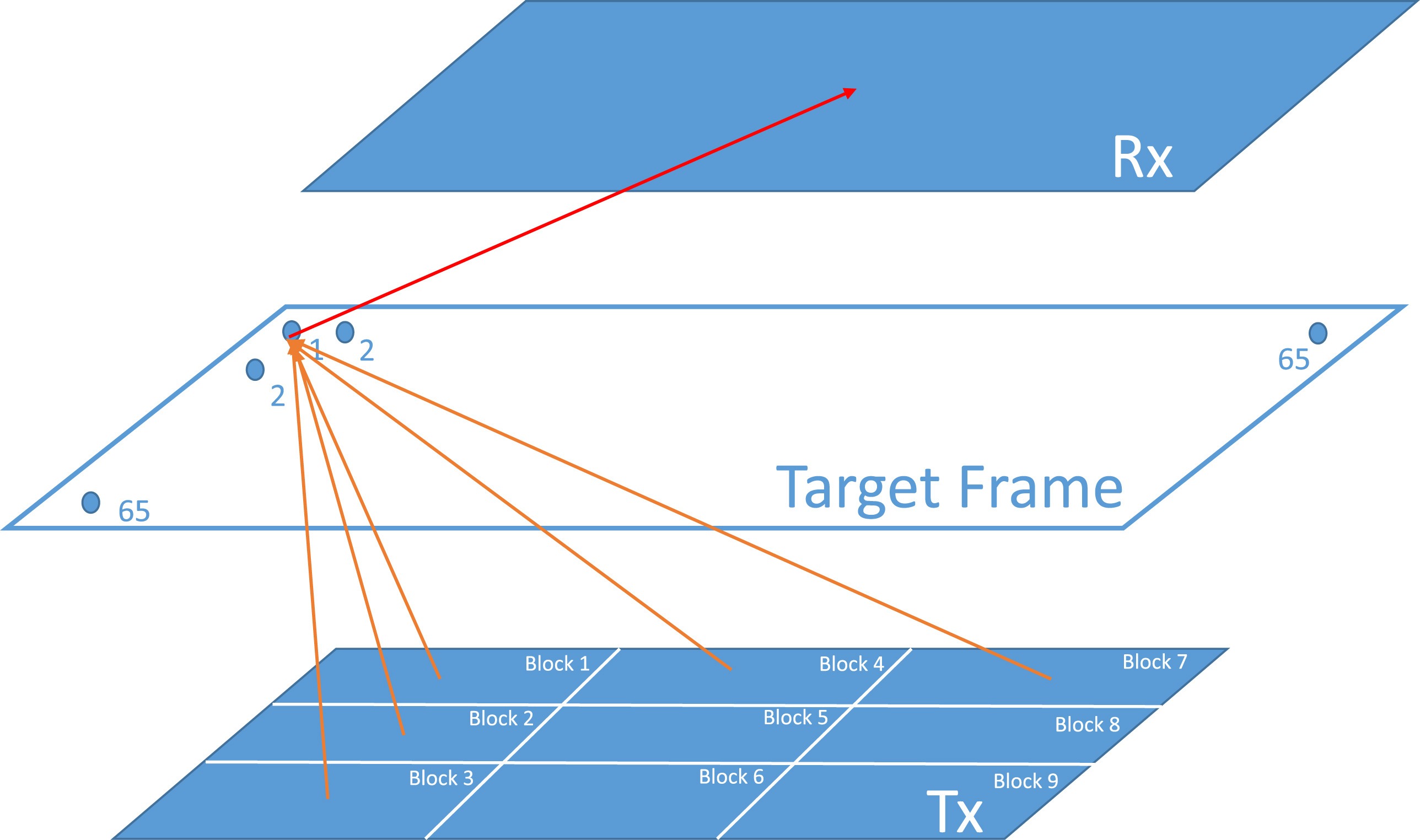
Design and simulation of a 2-D array flexible ultrasound transducer system fo...
Zhihua Gan, Brian Guo, Jiqi Cheng, Yi-Xian Qin
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2021.100106
2022, 100106
 摘要
摘要
Noninvasive diagnosis of bone density and mechanical properties using non-radiation imaging modality is an emerging area with promising in early prediction of osteopenia and treatment effectiveness in the clinic and functional disuse, i.e., long-term bedrest and space mission. Advances in quantitative ultrasound have shown advantages in measuring both bone density and mechanical strength, non-radiation, imaging capability, and easy to use. The challenge that remained is the poor penetration of ultrasound signals passing through trabecular and cortical bones and acoustic energy scattering. A new scanning confocal ultrasound technology is developed in this lab to detect the alteration of bone to provide diagnostic results in bone density and structure properties. A software-controlled flexible ultrasound system with 2-D dual array transducer is developed and proposed for the purpose of noninvasive bone density diagnosis and assessment of bone loss.
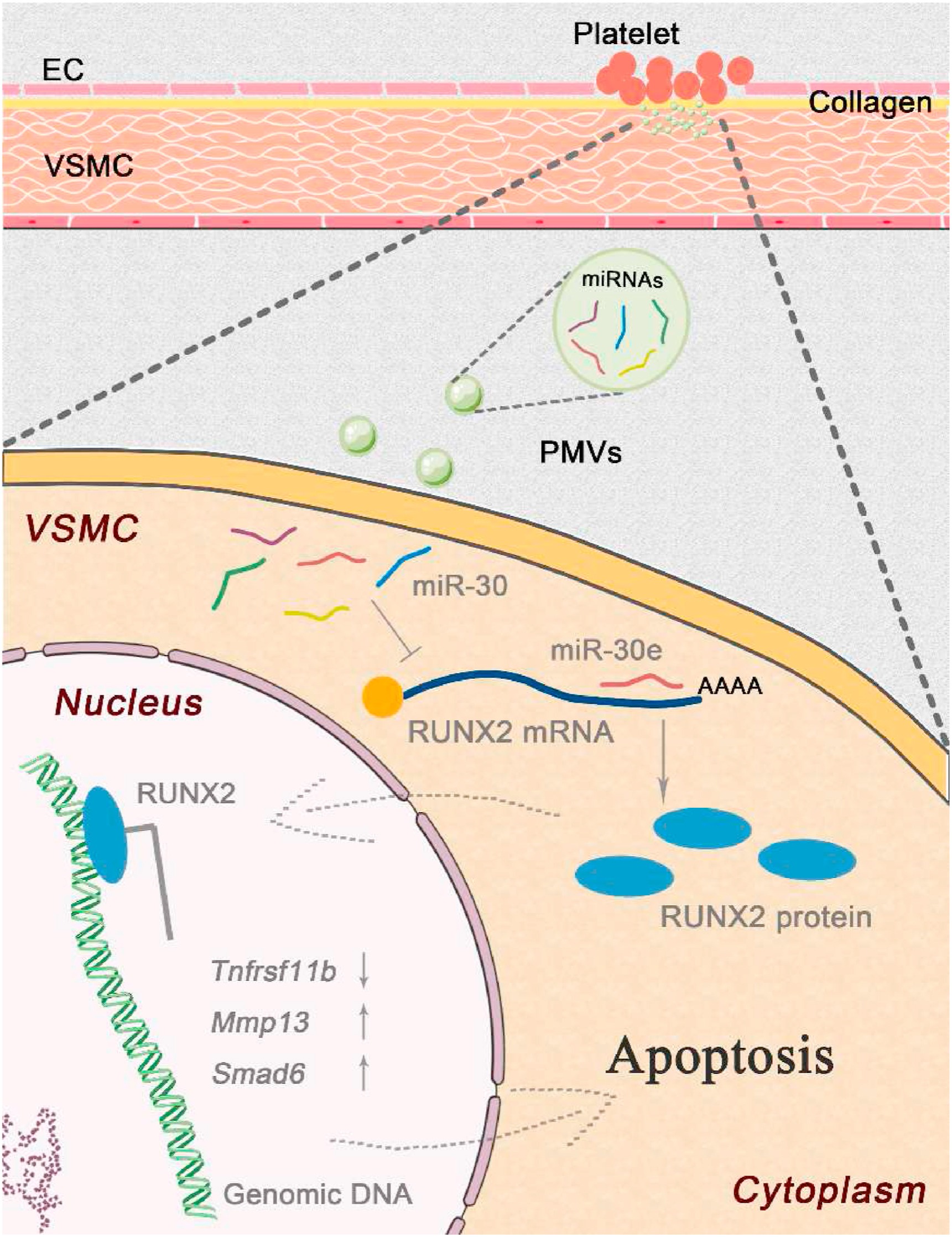
Platelet-derived microvesicles deliver miR-30e and promote VSMC apoptosis aft...
Li Zi-Tong, Chen Yuan-Xiu, Bao Han, Liu Ji-Ting, Zhuang Fei, Li Hai-Peng, Yao Qing-Ping, Jiang Zong-Lai, Qi Ying-Xin
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2021.100103
2022, 100103
 摘要
摘要
During vascular remodeling after intimal injury, circulating platelets are activated by exposed collagen and release platelet-derived microvesicles (PMVs), which may contribute to the injury-induced apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). However, the mechanisms in this process are still unclear. Using a rat balloon injury model, platelet adhesion at the injured site was detected, and promoted medial VSMC apoptosis was revealed with dT-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) in vivo. VSMC apoptosis was promoted by coincubation with PMVs in vitro. Transcriptomics analysis indicated the abound expression of the microRNA-30 (miR-30) family in platelets, and the expression of the miR-30 family in platelets and PMVs was confirmed with qPCR. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software identified transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) as a pivotal molecule linking miR-30 and cellular apoptosis.
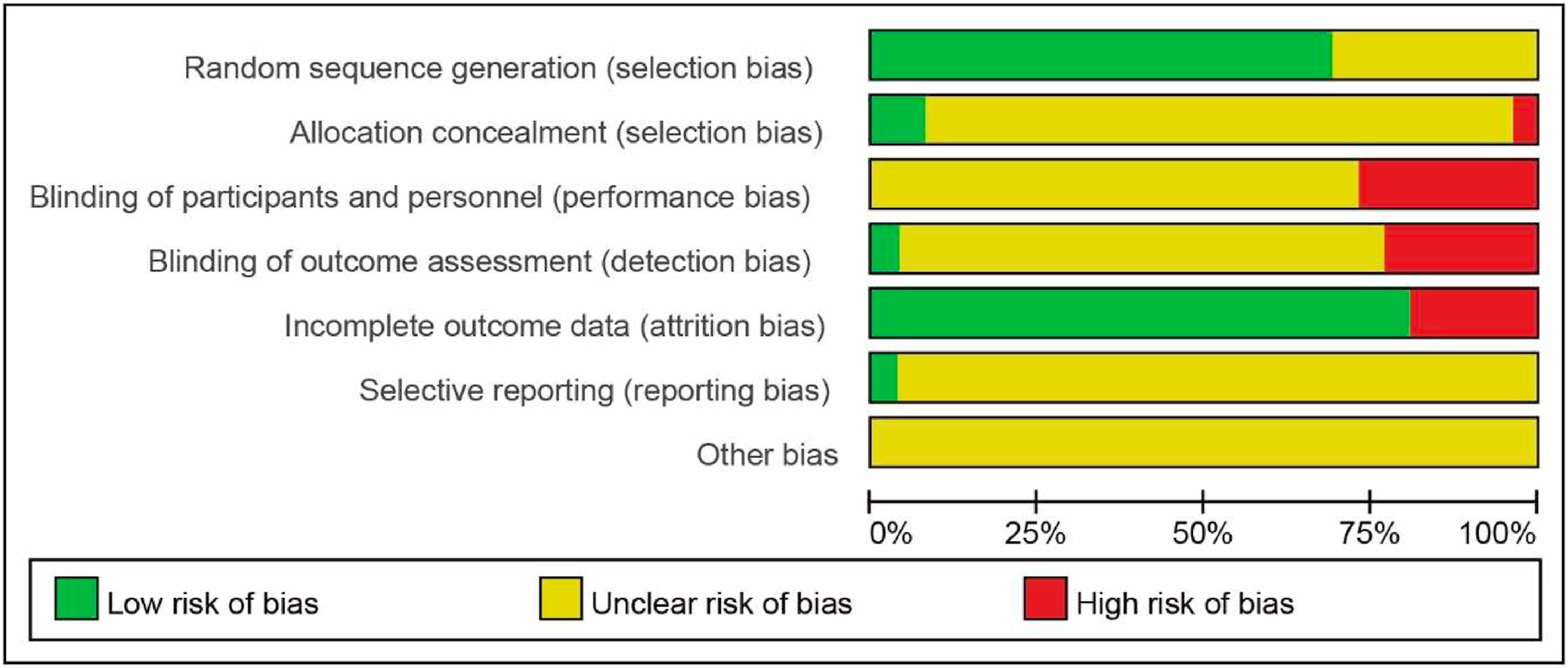
Traditional Chinese Medicine is effective for COVID-19: A systematic review a...
Jiayi Xu, Hongmei Liu, Yubo Fan, Baohua Ji
doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100139
2022, 100139
 摘要
摘要
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has played crucial roles in treating COVID-19 in China. But its effectiveness has not yet been widely realized/recognized over the world. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the clinical efficacy of TCM medicine in the treatment for COVID-19. We obtained the data of COVID-19 and traditional Chinese medicine from PubMed, MEDLINE, Web of Science and other databases, and searched from January 1, 2020 to January 26, 2022 to determine the randomized controlled trials (RCTs) without language restrictions. The review includes 26 randomized clinical trials including 2981 patients. The treatment of COVID-19 by TCM combined with conventional treatment is more effective than by pure conventional treatment in many aspects, including increasing of the effective rate [OR = 2.47, 95%CI (1.85, 3.30), P < 0.00001], fever disappearance rate [OR = 3.68, 95%CI (1.95, 6.96), P < 0.0001], fatigue disappearance rate
-
1
The role of mechanoreceptors in acupuncture
Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices2023,21(3)
-
2
MV-mediated biomineralization mechanisms and treatments of biomineralized dis...
Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices2023,21(3)
-
3
SR-AFU: super-resolution network using adaptive frequency component upsamplin...
Frontiers of Computer Science2023,21(3)
-
4
Unsupervised statistical text simplification using pre-trained language model...
Frontiers of Computer Science2023,21(3)
-
5
推力矢量型V/STOL飞行器动态过渡过程的操纵策略优化
航空动力学报2023,21(3)
-
6
耦合传热下激波对超声速气膜冷却影响
航空动力学报2023,21(3)
-
北京航空航天大学学报
-
北京航空航天大学学报(社会科学版)
-
复合材料学报
-
集成电路与嵌入式系统
-
航空学报
-
Chinese Journal of Aeronautics
-
航空动力学报
-
Frontiers of Computer Science
-
Propulsion and Power Research
-
Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices
-
Digital Twin
-
Electromagnetics Science and Technology
-
Congnitive Semantics
-
The Journal of the Air Transport Research Society
-
航空知识
-
问天少年
-
Chain
-
Virtual Reality & Intelligent Hardware
-
International Journal of Modeling Simulation and Scientific Computing
-
International Journal of Service and Computing Oriented Manufacturing
-
Mathematics in computer science
-
Atlantis Highlights in Engineering
-
Mathematical Blosciences and Engineering
-
Materials LAB
-
Journal of Economy and Technology
-
Digital Engineering
-
Guidance Navication and Control
-
Visual Computing for Industry Biomedicine and Art
-
图学学报